Posts Tagged: IIB
immediate interactive behavior (IIB)


Paper: Decade effects in mental addition
| The most important part of the Analytical Engine was undoubtedly the mechanical method of carrying the tens. (…) The difficulty did not consist so much in the more or less complexity of the contrivance as in the reduction of the time required to effect the carriage. (…) nothing but teaching the Engine to foresee and then to act upon that foresight could ever lead me to the object I desired… |
| Charles S. Babbage (1864), Passages from the Life of a Philosopher, p. 114 |
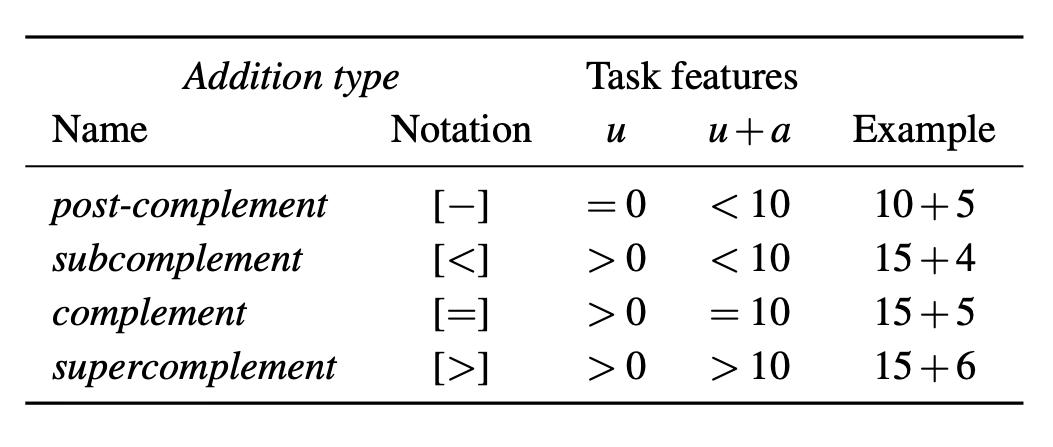
Classification of addition types for adding a single-digit addend a (with a∈{1…9}) to an augend Au (u denoting the augend’s unit). (See Table 1 for details.)
Hansjörg Neth, Stephen J. Payne
Decade effects in mental addition
We examine representational effects of Western numerals on mental arithmetic. An analysis of mental addition tasks using a base-10 place-value notation yields a taxonomy of addition types that is anchored in the notion of complements (i.e. additions with round sums). Two experimental studies use a paradigm of serial addition that presents lists of numbers to adult participants, who mentally represent all intermediate steps. In study 1, participants add sequences of single-digit addends in a self-paced fashion. Study 2 extends this paradigm by simultaneously presenting two addends, thus allowing for a modicum of strategic choice. Both studies vary the number of complements within the lists and measure addition accuracy and latency. Beyond decade and carry effects, our results show that lists containing or enabling complements are easier to add. Addition latencies jointly depend on addition type and problem size. When adders have some discretion about the order of choosing addends, they adaptively exploit the difficulty of addition types by tailoring their sequences to decade boundaries. One motivation for seeking complements lies in enabling subsequent post-complements. Reflecting on the dynamic interplay between numeric representations, strategic choices and cognitive adaptations, we discuss implications for psychological explanations, technology and design.
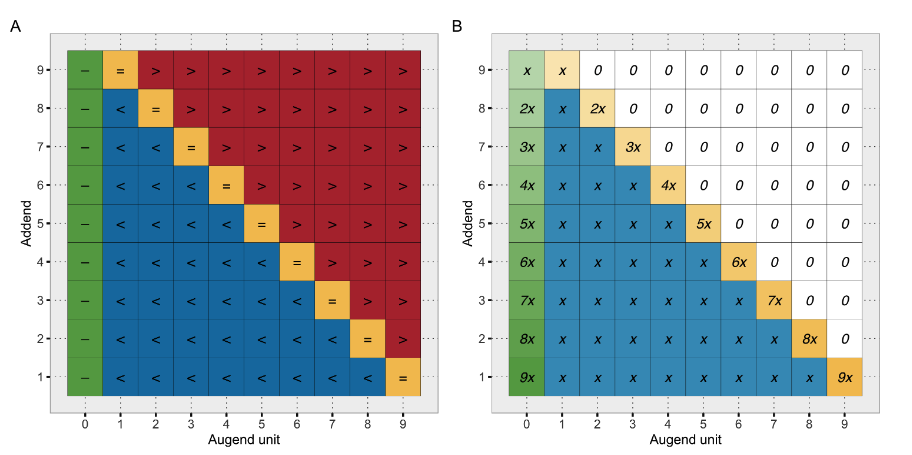
Four different addition types (A) and their hypothetical frequency (B, assuming uniform distribution of addends 1–9 and full decomposition of super-complements). (See Figure 4 in Appendix A1 for details.)
This article is part of the theme issue A solid base for scaling up: the structure of numeration systems.
Keywords: mental arithmetic, addition strategies, base notation, representational effects.
Reference: Neth, H., & Payne, S. J. (2025). Decade effects in mental addition. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 380, 20240220. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2024.0220
Related: Addition as interactive problem solving | Thinking by doing? | Immediate interactive behavior (IIB) | Arabic vs. Roman arithmetic | Taxonomy of actions | The cognitive basis of arithmetic | Interactive coin addition | The functional task environment
Resources: open access article | PDF download | Google Scholar


Paper: Visual working memory resources as item activation
Donald D. Hoffmann (1998), p. XII
and those involved in symbol manipulation and the organization of complex behaviors.
Ballard et al. (1997), p. 723
Bella Z. Veksler, Rachel Boyd, Christopher W. Myers, Glenn Gunzelmann, Hansjörg Neth, Wayne D. Gray
Visual working memory resources are best characterized as dynamic, quantifiable mnemonic traces

An example stimulus used in the paradigm of repeated serial search.
Abstract: Visual working memory (VWM) is a construct hypothesized to store a small amount of accurate perceptual information that can be brought to bear on a task. Much research concerns the construct’s capacity and the precision of the information stored. Two prominent theories of VWM representation have emerged: slot-based and continuous-resource mechanisms. Prior modeling work suggests that a continuous resource that varies over trials with variable capacity and a potential to make localization errors best accounts for the empirical data. Questions remain regarding the variability in VWM capacity and precision. Using a novel eye-tracking paradigm, we demonstrate that VWM facilitates search and exhibits effects of fixation frequency and recency, particularly for prior targets. Whereas slot-based memory models cannot account for the human data, a novel continuous-resource model does capture the behavioral and eye tracking data, and identifies the relevant resource as item activation.
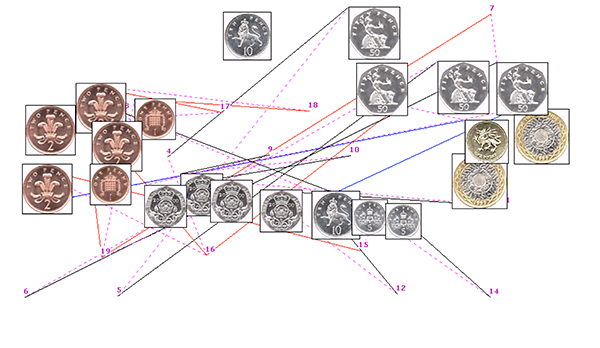
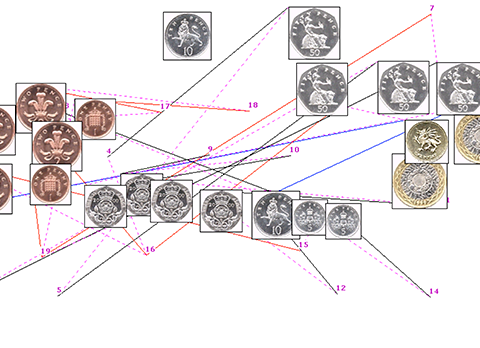
Paper: Interactive coin addition
| ‘Can you do Addition?’ the White Queen asked. ‘What’s one and one and one and one and one and one and one and one and one and one?’ ‘I don’t know,’ said Alice. ‘I lost count.’ |
| Lewis Carroll, Through the Looking-Glass, Chapter IX. |
Hansjörg Neth, Stephen J. Payne
Interactive coin addition: How hands can help us think
Abstract: Does using our hands help us to add the value of a set of coins?

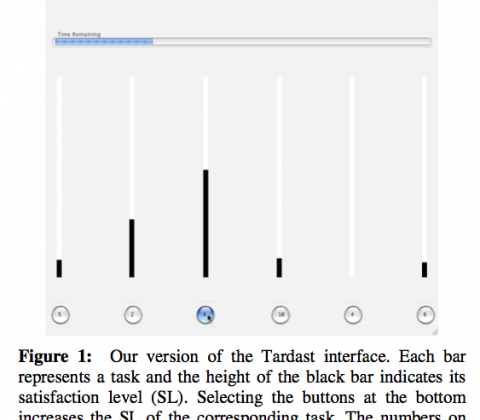
Paper: Feedback design for controlling a dynamic multitasking system
| If an organism is confronted with the problem of behaving approximately rationally, or adaptively, in a particular environment, the kinds of simplifications that are suitable may depend not only on the characteristics—sensory, neural, and other—of the organism, but equally on the nature of the environment. |
| H.A. Simon (1956), Rational choice and the structure of the environment, p. 130 |
Hansjörg Neth, Sangeet S. Khemlani, Wayne D. Gray
Feedback design for the control of a dynamic multitasking system: Dissociating outcome feedback from control feedback
Objective: We distinguish outcome feedback from control feedback to show that suboptimal performance in a dynamic multitasking system may be caused by limits inherent to the information provided rather than human resource limits.