Posts Tagged: IIB
immediate interactive behavior (IIB)
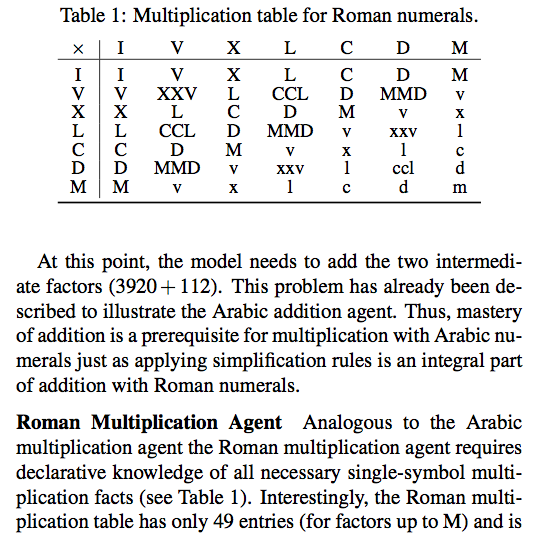

Paper: Arithmetic with Arabic vs. Roman numerals
| … how information is represented can greatly affect how easy it is to do different things with it. (…) it is easy to add, to subtract, and even to multiply if the Arabic or binary representations are used, but it is not at all easy to do these things — especially multiplication — with Roman numerals. This is a key reason why the Roman culture failed to develop mathematics in the way the earlier Arabic cultures had. |
| D Marr (1982): Vision, p. 21 |
Dirk Schlimm, Hansjörg Neth
Modeling ancient and modern arithmetic practices: Addition and multiplication with Arabic and Roman numerals
Abstract: To analyze the task of mental arithmetic with external representations in different number systems we model algorithms for addition and multiplication with Arabic and Roman numerals. This demonstrates that Roman numerals are not only informationally equivalent to Arabic ones but also computationally similar — a claim that is widely disputed. An analysis of our models’ elementary processing steps reveals intricate trade-offs between problem representation, algorithm, and interactive resources. Our simulations allow for a more nuanced view of the received wisdom on Roman numerals. While symbolic computation with Roman numerals requires fewer internal resources than with Arabic ones, the large number of needed symbols inflates the number of external processing steps.
Paper: Immediate interactive behavior (IIB)
| … immediate behavior, responses that must be made to some stimulus within very approximately one second (that is, roughly from ~300 ms to ~3 sec). (…) … immediate behavior is where the architecture shows through — where you can see the cognitive wheels turn and hear the cognitive gears grind. Immediate behavior is the appropriate arena in which to discover the nature of the cognitive architecture. |
| A. Newell (1990), Unified theories of cognition, p. 235f. |
Hansjörg Neth, Richard A. Carlson, Wayne D. Gray, Alex Kirlik, David Kirsh, Stephen J. Payne
Immediate interactive behavior: How embodied and embedded cognition uses and changes the world to achieve its goals
Summary: We rarely solve problems in our head alone. Instead, most real-world problem solving and routine behavior recruits external resources and achieves its goals through an intricate process of interaction with the physical environment. Immediate interactive behavior (IIB) entails all adaptive activities of agents that routinely and dynamically use their embodied and environmentally embedded nature to augment cognitive processes. IIB also characterizes an emerging domain of cognitive science research that studies how cognitive agents exploit and alter their task-environments in real-time. Examples of IIB include arranging coins when adding their values, solving a problem with paper and pencil, arranging tools and ingredients while preparing a meal, programming a VCR, and flying an airplane.
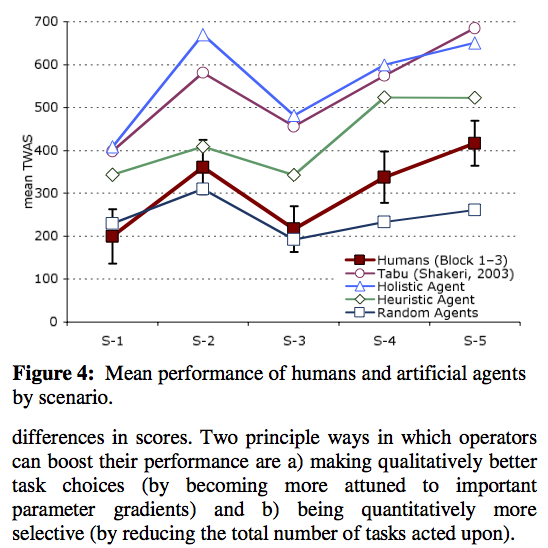
Paper: Juggling multiple tasks in a synthetic task environment
| Doing two things at once, like singing while you take a shower, is not the same as instant messaging while writing a research report. Don’t fool yourself into thinking you can multitask jobs that need your full attention. You’re not really having a conversation while you write; you’re shifting your attention back and forth between the two activities quickly. You’re juggling. When you juggle tasks, your work suffers AND takes longer — because switching tasks costs. |
| Gina Trapani, Work Smart, FastCompany.com |
Hansjörg Neth, Sangeet S. Khemlani, Brittney Oppermann, Wayne D. Gray
Juggling multiple tasks: A rational analysis of multitasking in a synthetic task environment
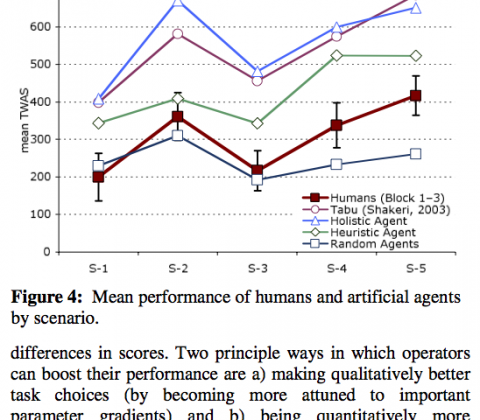
Abstract: Tardast (Shakeri 2003; Shakeri & Funk, in press) is a new and intriguing paradigm to investigate human multitasking behavior, complex system management, and supervisory control. We present a replication and extension of the original Tardast study that assesses operators’ learning curve and explains gains in performance in terms of increased sensitivity to task parameters and a superior ability of better operators to prioritize tasks. We then compare human performance profiles to various artificial software agents that provide benchmarks of optimal and baseline performance and illustrate the outcomes of simple heuristic strategies. Whereas it is not surprising that human operators fail to achieve an ideal criterion of performance, we demonstrate that humans also fall short of a principally achievable standard. Despite significant improvements with practice, Tardast operators exhibit stable sub-optimal performance in their time-to-task allocations.
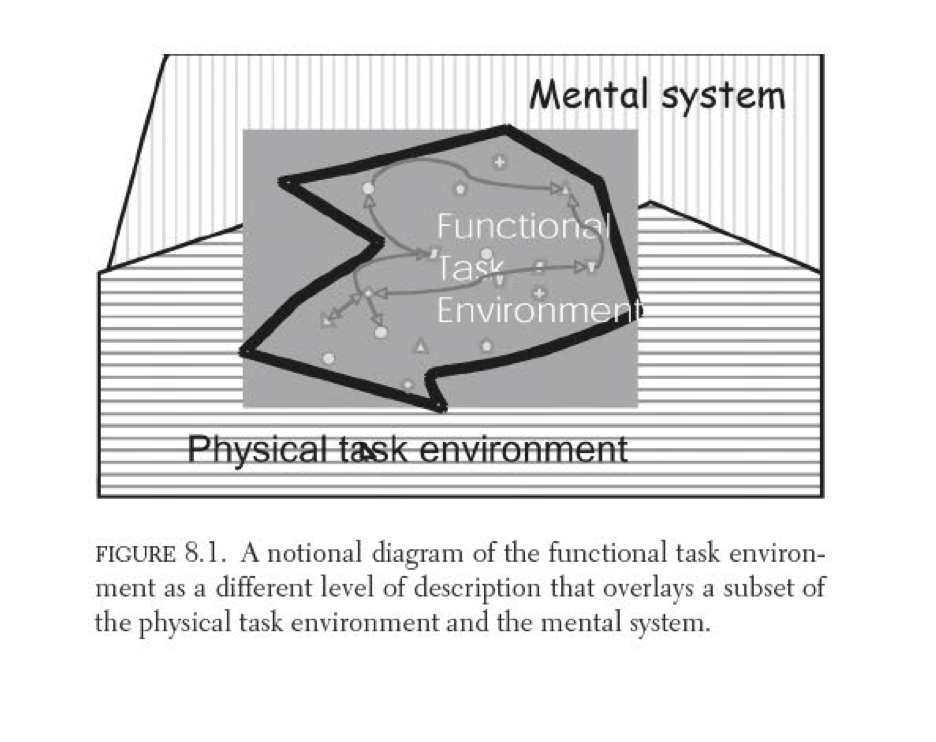
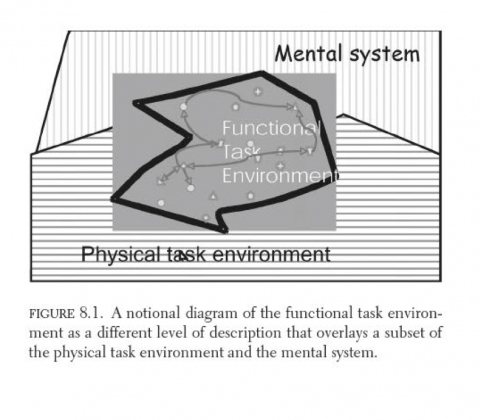
Chapter: The functional task environment
The apparent complexity of our behavior over time is largely a reflection
of the complexity of the environment in which we find ourselves.
(Simon, 1996, p. 53)
Wayne D. Gray, Hansjörg Neth, Michael J. Schoelles
The functional task environment
From the introduction: Although human thought may be possible in those floatation tanks that are used to encourage meditative states, in by far the majority of instances thought occurs in the context of some physical task environment. The physical environment can be as simple as a light and book. It can be as complex as the face of a mountain and the equipment of the climber. It may be as dynamic as the cockpit of an F-16 in supersonic flight and as reactive as a firefight in Iraq or as heated as an argument between lovers.