Posts Tagged: theory
Paper: Perspectives on the 2×2 Matrix
Hansjörg Neth, Nico Gradwohl, Dirk Streeb, Daniel A. Keim, Wolfgang Gaissmaier
Perspectives on the 2×2 matrix: Solving semantically distinct problems based on a shared structure of binary contingencies
Abstract
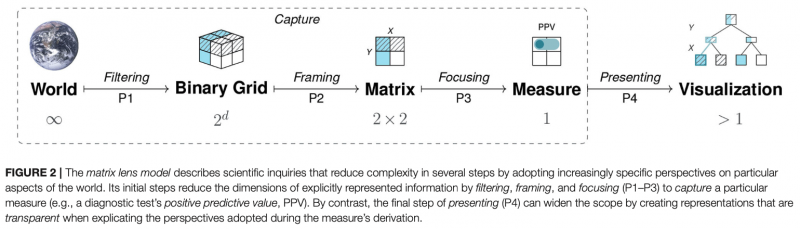
Cognition is both empowered and limited by representations. The matrix lens model explicates tasks that are based on frequency counts, conditional probabilities, and binary contingencies in a general fashion. Based on a structural analysis of such perspective on representational accounts of cognition that recognizes representational isomorphs as opportunities, rather than as problems.
The shared structural construct of a 2×2 matrix supports a set of generic tasks and semantic mappings that provide a tasks, the model links several problems and semantic domains and provides a new unifying framework for understanding problems and defining scientific measures. Our model’s key explanatory mechanism is the adoption of particular perspectives on a 2×2 matrix that categorizes the frequency counts of cases by some condition, treatment, risk, or outcome factor. By the selective steps of filtering, framing, and focusing on specific aspects, the measures used in various semantic domains negotiate distinct trade-offs between abstraction and specialization. As a consequence, the transparent communication of such measures must explicate the perspectives encapsulated in their derivation.
To demonstrate the explanatory scope of our model, we use it to clarify theoretical debates on biases and facilitation effects in Bayesian reasoning and to integrate the scientific measures from various semantic domains within a unifying framework. A better understanding of problem structures, representational transparency, and the role of perspectives in the scientific process yields both theoretical insights and practical applications.
Why read this paper?
This paper is quite long and covers a wide array of concepts and topics. So what can you expect to gain from reading it?


Paper: Rational task analysis (RTA)
a theory of thinking and problem solving cannot predict behavior
unless it encompasses both an analysis of the structure of task environments
and an analysis of the limits of rational adaptation to task requirements.
(Newell & Simon, 1972, p. 55)
Hansjörg Neth, Chris R. Sims, Wayne D. Gray
Rational task analysis: A methodology to benchmark bounded rationality
Abstract: How can we study bounded rationality? We answer this question by proposing rational task analysis (RTA)—a systematic approach that prevents experimental researchers from drawing premature conclusions regarding the (ir-)rationality of agents. RTA is a methodology and perspective that is anchored in the notion of bounded rationality and aids in the unbiased interpretation of results and the design of more conclusive experimental paradigms.
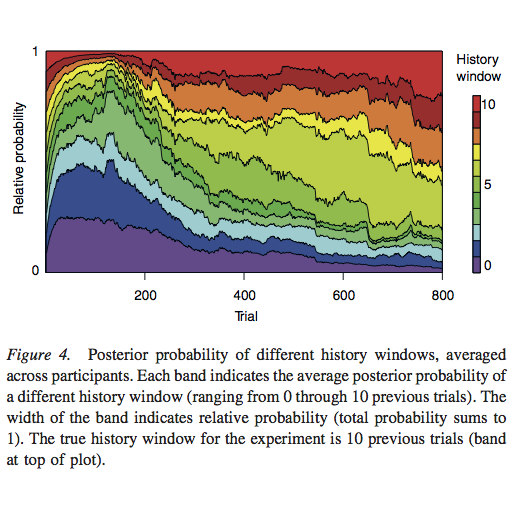
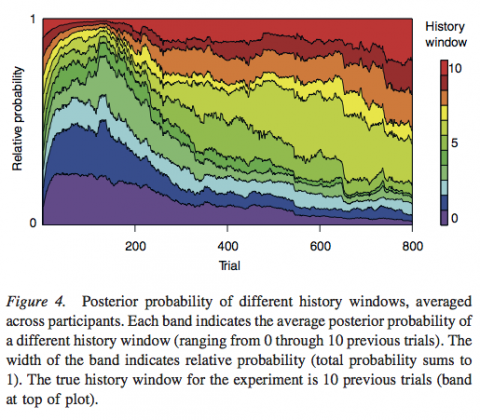
Paper: Melioration as rational choice
Melioration (…) is the dynamic process controlling allocation of time across response alternatives.
Herrnstein & Vaughan (1980). Melioration and behavioral allocation, p. 143+172
Chris R. Sims, Hansjörg Neth, Robert A. Jacobs, Wayne D. Gray
Melioration as rational choice: Sequential decision making in uncertain environments
Abstract: Melioration — defined as choosing a lesser, local gain over a greater longer term gain — is a behavioral tendency that people and pigeons share. As such, the empirical occurrence of meliorating behavior has frequently been interpreted as evidence that the mechanisms of human choice violate the norms of economic rationality. In some environments, the relationship between actions and outcomes is known. In this case, the rationality of choice behavior can be evaluated in terms of how successfully it maximizes utility given knowledge of the environmental contingencies. In most complex environments, however, the relationship between actions and future outcomes is uncertain and must be learned from experience. When the difficulty of this learning challenge is taken into account, it is not evident that melioration represents suboptimal choice behavior.