Posts in Category: conference
Paper: simBorgs modeling dynamic decision making
| For the exogenously extended organizational complex functioning as an integrated homeostatic system unconsciously, we propose the term “cyborg”. |
| M.E. Clynes and N.S. Kline (1960), Cyborgs and Space (Astronautics, 13) |
Christopher W. Myers, Hansjörg Neth, Michael J. Schoelles, Wayne D. Gray
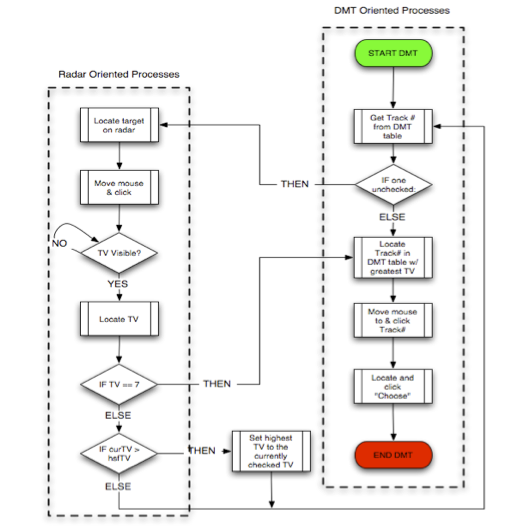
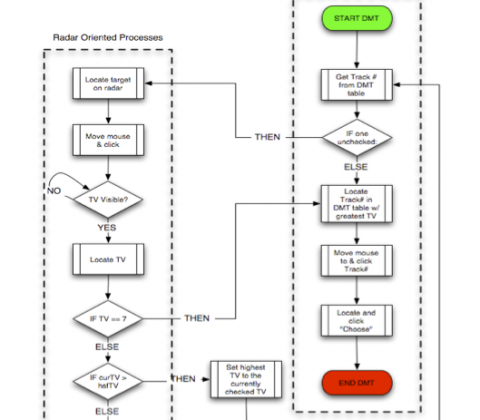
The simBorg approach to modeling a dynamic decision-making task
Abstract: The simulated cyborg (or, simBorg) approach blends computational embodied-cognitive models of interactive behavior with artificial intelligence based components in a simulated task environment (Gray, Schoelles, & Veksler, 2004). simBorgs combine human and machine components. This combination of high fidelity cognitive modeling (human) and AI (machine) facilitates the development of families of models that allow the modeler to hold components (memory, vision, etc) at different levels of expertise without concern for cognitive plausibility. For example, rather than modeling human problem solving, the modeler can rely on various black-box techniques (i.e., cognitively implausible AI), thereby focusing on predicting how subtle differences in costs and benefits in interactive methods affect performance and errors. The current modeling endeavor adopts the simBorg approach in order to build a family of interactive decision-making agents.

Paper: Searching for counterexamples
| If it was so, it might be; and if it were so, it would be; but as it isn’t, it ain’t. That’s logic. |
| Tweedledee (Lewis Carroll, Through the Looking Glass and what Alice found there, 1872) |
Hansjörg Neth, Philip N. Johnson-Laird
The search for counterexamples in human reasoning
Research question: A major point of contention about human reasoning is whether or not individuals search for counterexamples to conclusions. According to theorists who argue that the mind is equipped with tacit rules of inference, the decision that an argument is invalid depends on a failure to find a derivation leading from the premises to the conclusion (see e.g., Rips, 1994). However, with this procedure, one can never be cer- tain that the space of possible derivations has been searched exhaustively. Alternatively, reasoners may base their inferences on mental models (Johnson-Laird and Byrne, 1991). This theoretical account rests on the semantic principle of validity: a conclusion is valid if and only if it allows for no counterexamples, i.e., possibilities in which the premises are true but the conclusion is false. Hence, by constructing a counterexample, reasoners are able to know that an inference is invalid.
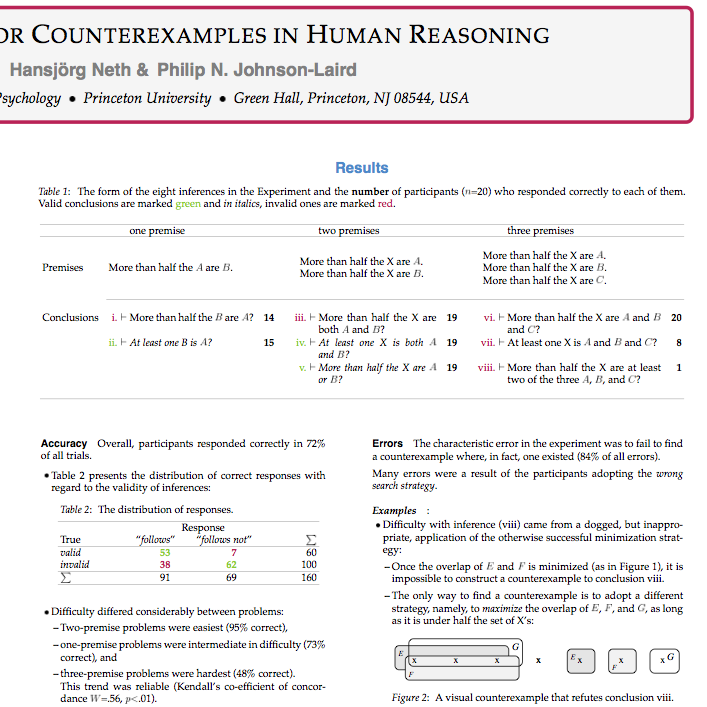
Method: To search for a search for counterexamples, we carried out an experiment in which the participants had to evaluate eight inferences based on non-standard quantifiers. Quite common in everyday life, such inferences call for a higher-order predicate calculus, which is incomplete.
Results: A striking phenomenon was the participants’ spontaneous use of a variety of strategies. In 80% of all trials, they constructed a single specific instance of the premises. Typically, the participants constructed a diagram in which they tried to minimize the overlap between the given sets. Indeed, every single participant came up with at least one counterexample. Our study has shown (…) that logically naive individuals do spontaneously search for counterexamples for at least one sort of deduction.
Keywords: Logic, thinking and reasoning, syllogisms with non-standard quantifiers, mental model theory, counterexamples.
Reference: Neth, H., & Johnson-Laird, P. N. (1999). The search for counterexamples in human reasoning. In M. Hahn, & S. C. Stoness (Eds.), Proceedings of the 21st Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (p. 806). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Related: Suppression effects | Diploma thesis
Resources: Download PDF | Google Scholar
